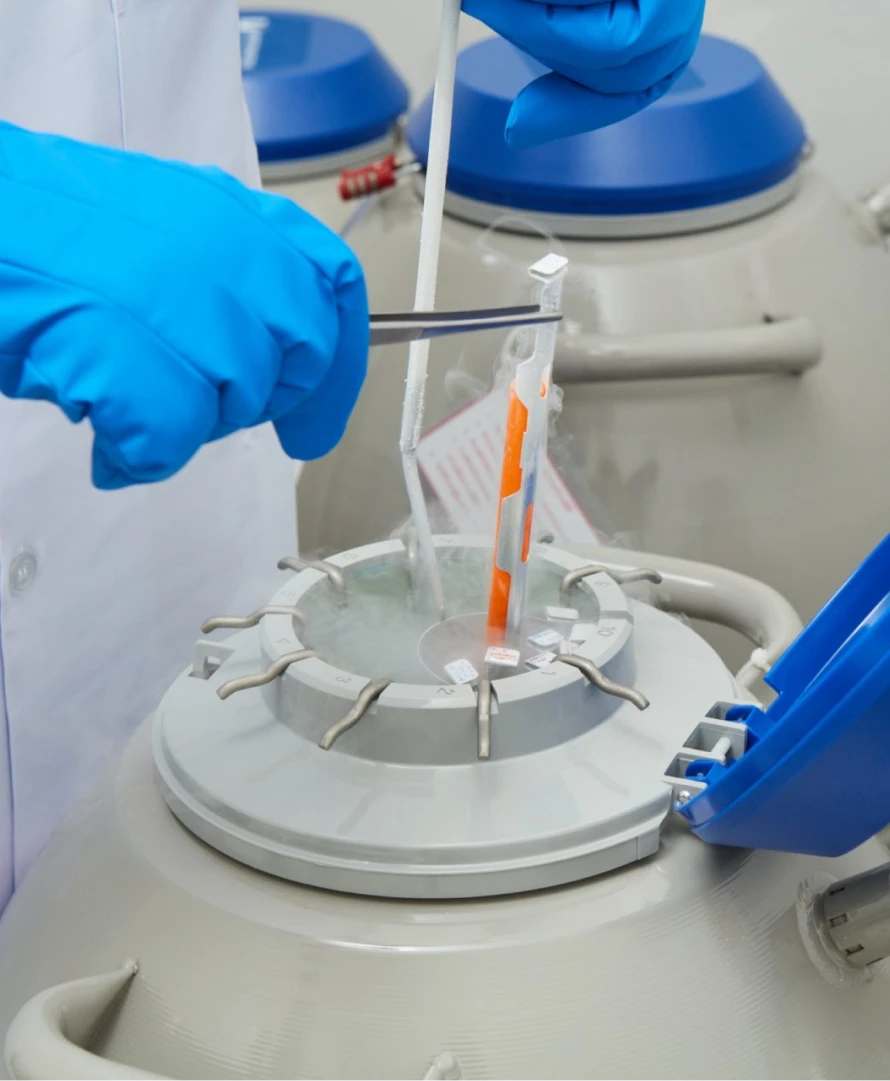
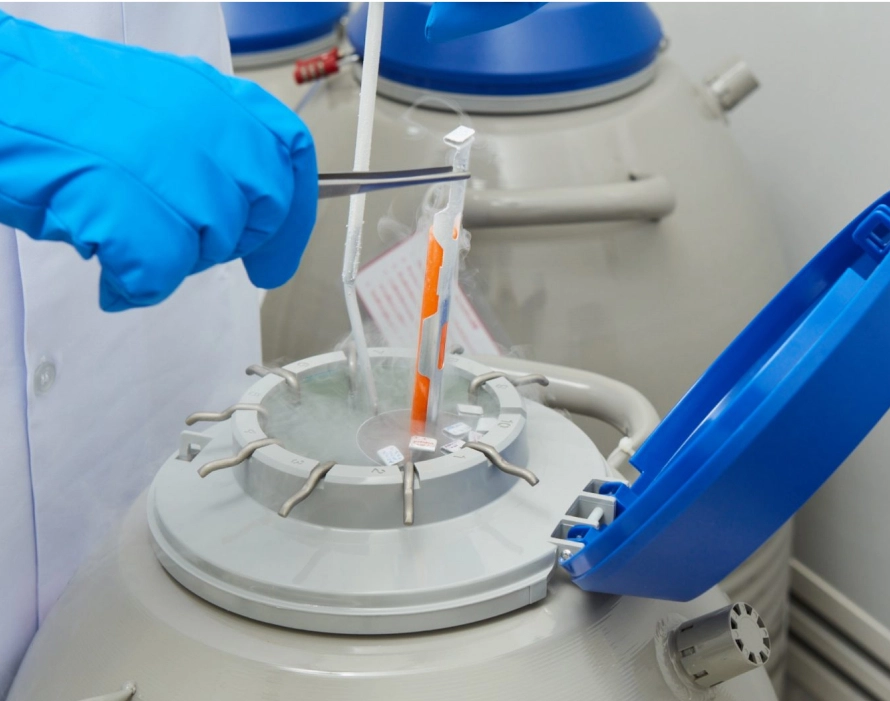
Fertility Preservation


The number of eggs, sperm, or embryos that can be preserved depends on the quantity of eggs in a given cycle and the overall health of the male or female. Egg preservation is generally more popular than sperm preservation because women have a limited time frame in which they can store high-quality eggs due to age-related fertility decline.
Egg preservation is ideal for women who are not yet ready for marriage or pregnancy, as well as for women who are about to undergo treatments that may affect the quantity and quality of their eggs or reproductive system. This includes those undergoing cancer treatment, such as chemotherapy or radiation, women needing to have their ovaries removed, or those with genetic conditions that cause premature ovarian failure. Therefore, egg preservation provides a valuable option for couples to plan for future parenthood.
Egg Freezing Procedure Details
Sperm and Embryo Freezing Procedure Details