[vc_row full_width=”stretch_row_1200 td-stretch-content”][vc_column tdc_css=”eyJhbGwiOnsibWFyZ2luLWJvdHRvbSI6IjAiLCJkaXNwbGF5IjoiIn19″][td_block_title f_header_font_size=”75″ block_template_id=”td_block_template_5″ custom_title=”PGT Testing and Karyomapping Technology” tdc_css=”eyJhbGwiOnsibWFyZ2luLWJvdHRvbSI6IjAiLCJkaXNwbGF5IjoiIn19″ f_header_font_line_height=”0.75″ header_text_color=”#f15361″][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row full_width=”stretch_row_1200 td-stretch-content”][vc_column][vc_column_text f_post_font_family=”file_2″ post_color=”#6b6b6b” f_post_font_size=”24″]

[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row full_width=”stretch_row_1200 td-stretch-content”][vc_column width=”1/1″][vc_column_text f_post_font_family=”file_2″ f_h1_font_family=”file_3″ f_post_font_size=”24″ post_color=”#666666″]
Inspire IVF’s Platform.
The term PGT, Preimplantation Genetic Testing, is often loosely used to refer to any testing performed on an embryo prior to it being transferred to the uterus. The process is also called aneuploidy screening.
Advances in genetic analysis tools for molecular diagnostics are revolutionizing the practice of medicine, improving prenatal and reproductive care, enabling earlier disease detection, and advancing treatment of heritable diseases.
Thanks to Preimplantation Genetic Testing and Screening that we offer at Inspire IVF, couples, who are concerned for their future children’s health, can gain peace of mind.
In the course of the in vitro fertilization procedure, embryos are tested for chromosomal, genetic and hereditary disorders and only those without any defects are transferred into the uterus.
Our diagnosis provides many couples with the chance of having a healthy offspring.

Who should have PGT Testing?
PGT testing offers many benefits, mainly the reassurance that normal embryos are being transferred. Inspire IVF specifically recommends testing as appropriate for those with:
-
- Advanced maternal age (>35 years)
-
- History of recurrent miscarriage
-
- Recurrent Implantation failure
-
- Previous pregnancy with foetal/chromosomal abnormality
-
- Risk of passing on a single gene disorder
-
- Risk of an X-linked disorder
-
- An altered sex chromosome complement (eg: XXY)
-
- Carrier of a balanced chromosome rearrangement
What is the difference between PGD and PGS?
Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) is a method which allows us to eliminate the risk of passing on genetic disorders to a child before the woman gets pregnant. By examining the embryo’s cells, we are able to determine whether it has any DNA defects. For some couples it is the only possibility for having healthy offspring.
Preimplantation Genetic Screening (PGS) is the proper term for testing for overall chromosomal normalcy in embryos by examining the embryo cells. PGS is not looking for a specific disease diagnosis – it is screening the embryo for normal chromosome copy number.
OUR PLATFORM
Inspire IVF uses the Illumina Platform for testing of all suitable embryos. Illumina platforms have been widely used internationally in PGS/PGD, pregnancy chromosome examination, Noninvasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT), hereditary disease detection and other fields.
Illumina’s genomics solution, using NGS and advanced SNP array technology, produces fast and accurate genome information in clinical diagnosis.
NEXT GENERATION SEQUENCING (NGS)
The PGD NGS method (Pre Implantation Diagnosis based on the Next Generation Sequencing platform) uses the most up-to-date techniques of human genome sequencing (reading of genetic information) for testing embryos and opens new diagnostic possibilities.
It is used as a part of in vitro fertilization procedure if the client requires, and provides comprehensive information concerning each embryo’s DNA for diseases or genetic mutations. It provides our physicians with a unique opportunity to help couples who are exposed to an increased risk of genetic abnormalities in the foetus. This is the first solution of this kind in the world.
The main advantage of the new PGS-NGS technology is its extraordinary sensitivity and precision. Test design is tailored to the needs of a given patient after consultation with our clinicians.
NGS has been applied in comprehensive chromosome screening, improving the implantation rate of embryos. NGS can conduct a parallel sequence determination to hundreds of thousands to millions of DNA molecules at once, which is the most advanced technology used in genetic testing across the world.
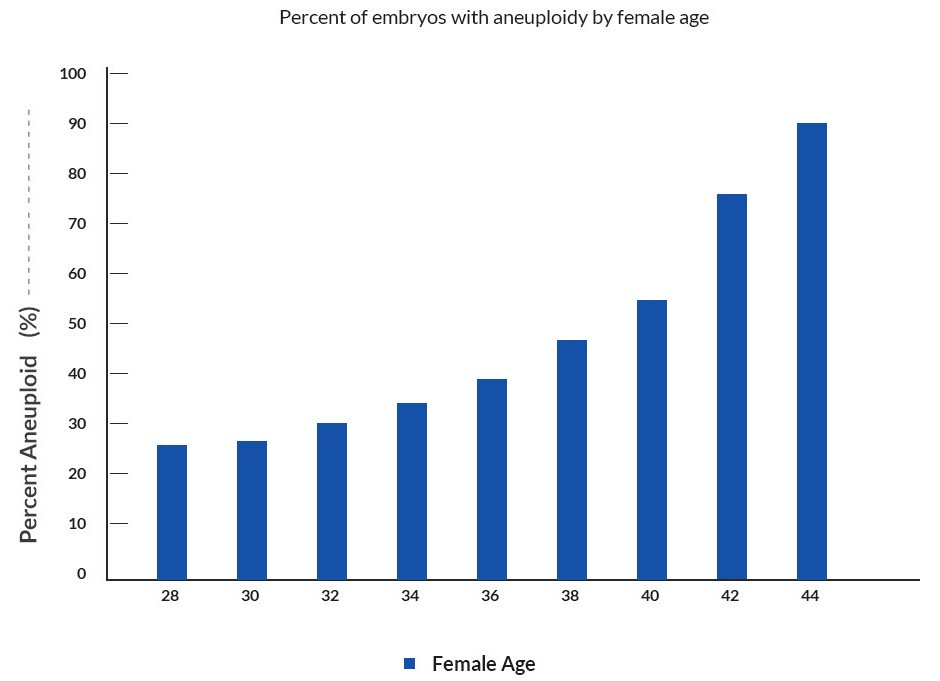
Chromosomal Abnormalities according to Female Age
Human eggs are often chromosomally abnormal – and the percentage of eggs with a chromosomal abnormality increases with increasing female age. In general, about 30-60% of human embryos have some type of chromosomal abnormality. This increases significantly with advancing female age, as shown in the chart below.
Advantage of NGS Technology
-
- Tests all 24 chromosomes simultaneously with unprecedented accuracy – at a level of 99.999%
-
- Tests for a variety of monogenic diseases with known genetic background.
-
- Embryo safety – reducing the number of biopsies for the diagnosis.
Usually just one embryo biopsy is sufficient to obtain a reliable result. In the case of existing methods, occasionally, the biopsy and the test has to be repeated.
- Embryo safety – reducing the number of biopsies for the diagnosis.
-
- Until now it was not possible to combine chromosomal aneuploidy and monogenic diseases tests. Today, due to NGS it is possible. Just one embryo biopsy will suffice.
-
- NGS method is considered to be referential for all the other techniques.
DNA sequencing is referred to as the reference method (model for others), mainly due to the direct nature of the genetic material reading. Other methods (FISH and microarrays) use markers and light as change markers and indirectly test the genetic material. For this reason, these methods are currently being abandoned in favour of the use of NGS.
- NGS method is considered to be referential for all the other techniques.
SINGLE NUCLEOTIDE POLYMORPHISM (SNP Array)
As chromosome problems in embryos is the major cause of IVF failure and premature pregnancy loss, Illumina’s SNP array platform can significantly improve the success rate of embryo implantation and reduce the risk of miscarriage.
PGS is thought to increase success rates for IVF in women over 35, as well as those who have suffered repeated IVF failure or recurrent miscarriage. Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) analysis allows testing of all 23 pairs of chromosomes.
At Inspire IVF we offer SNP analysis because it tests for both copy number changes and inversions and translocations.
What is the risk for having a chromosomally abnormal baby for couples that do not have PGS with their IVF?
In humans there is a natural selection process that prevents implantation of abnormal embryos. The large majority of chromosomally abnormal embryos will arrest in early development and not survive long enough to implant in the uterus.
Some will implant and result in early miscarriage. An extremely small percentage can continue further into pregnancy and could progress to a live birth of a chromosomally abnormal baby – if not detected during pregnancy.
By testing the chromosomes of embryos available, we can identify and discard embryos with abnormal chromosomal arrangements and pick the embryo(s) for transfer which have normal chromosomes.
In the general population, the risk for a live birth with a chromosomal abnormality is:
| Female age | Risk of a live birth with any chromosomal abnormality |
| 25 | 1/476 |
| 30 | 1/385 |
| 35 | 1/164 |
| 40 | 1/51 |
| 45 | 1/15 |
Advantage of SNP Array
In molecular biology, SNP array is a type of DNA microarray which is used to detect polymorphisms within a population. A single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP), a variation at a single site in DNA, is the most frequent type of variation in the genome. Around 325 million SNPs have been identified in the human genome, 15 million of which are present at frequencies of 1% or higher across different populations worldwide.
-
- SNP Array can detect all chromosomal abnormalities, covering 23 pairs of chromosomes, while the traditional FISH technology can only cover 5-7 pairs of chromosomes
-
- SNP Array has a higher detection credibility to embryonic aneuploidies.
-
- With high precision, auto detection and analysis, it has an accurate detection rate of more than 99.9%.
-
- On the basis of the detection of chromosome aneuploidies, SNP Array can also detect the located recurring deletion of chromosome segment, thus detect non-balanced chromosomes.
-
- With a wide application scope, it supports diagnosis for polar bodies, blastomeres, blastocyst trophectoderm cells and a variety of biopsy materials. With a stable and mature technology, it has been widely applied among the world’s leading PGD centres.
-
- It can accurately eliminate genetic diseases, particularly single gene disorders.
KARYOMAPPING
What is Karyomapping?
Karyomapping is a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) test that uses a DNA finger-printing technique to identify which embryos have inherited an altered gene.
Karyomapping is a technique that allows couples – known to be carriers of an inherited condition – to avoid passing on that disorder on to their offspring.
DNA samples are collected, usually via a simple blood test, from the couple and other family members whose genetic status for the disease is known. Preliminary testing of those samples using Karyomapping allows a DNA fingerprint in the region of the faulty gene to be determined.
After this, as part of an IVF cycle, embryos are formed from the couples eggs and sperm. Embryo biopsy is performed on the embryos and the cells are tested for the DNA fingerprint, revealing those embryos that have inherited the altered gene. If the fingerprint characteristic of the healthy embryo is detected, then the embryo is free of the genetic disorder and suitable for transfer to the woman’s uterus during an IVF cycle.
Karyomapping also provides information across the entire genome, meaning we can identify some of the chromosomal errors that cause implantation failure and miscarriage.
Karyomapping therefore has the potential to help us identify the embryos that have the best chance of pregnancy success, which will improve our live birth rates for couples accessing this treatment.
Who is karyomapping suitable for?
Karyomapping is suitable for Inspire IVF clients who know that they a carrier of a genetic disorder. They may already have an affected child, be aware of a family history of the disorder, or have had their DNA tested to confirm that they carry a defective gene.
How does Karyomapping work?
A blood sample is taken from the father, the mother and one or more relatives who are affected by (or carriers of) a particular disorder. The relatives used may be an affected child, or the parents of the couple. These relatives are referred to as ‘references’.
Karyomapping looks at the chromosomes, the rod-like structures that are found in cells and contain the genes. Karyomapping examines the chromosomes of the mother, father and the reference at 300,000 different points, looking for features characteristic of the defective chromosome. Essentially, karyomapping finds a fingerprint that is unique to the chromosome that carries the defective gene. It is then possible to test embryos produced using IVF for this presence of this fingerprint. Whenever the fingerprint is seen in an embryo, it means that it has inherited the chromosome carrying the defective gene.
If the fingerprint characteristic of the chromosome carrying the defective gene is not detected then it can be inferred that the embryo has inherited normal copies of the gene and is therefore likely to be free of the disorder. Embryos of this type are good candidates for embryo transfer.
Like all tests involving analysis of embryos, karyomapping should be considered a way of reducing the risk of having an affected pregnancy, not an absolute guarantee.
Karyomapping is used to test a small number of cells taken from an embryo before it is transferred to the uterus. A test carried out on such a minute amount of tissue can never be 100% accurate. In most cases, the chance of Karyomapping successfully detecting an embryo affected by a specific inherited disorder is better than 95%.

[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text f_h2_font_family=”file_2″ f_post_font_family=”file_2″ post_color=”#ffffff” h_color=”#ffffff” tdc_css=”eyJhbGwiOnsibWFyZ2luLWJvdHRvbSI6IjAiLCJkaXNwbGF5IjoiIn19″ f_post_font_size=”24″ f_h2_font_size=”40″]
Contact Form
Our Fertility specialists are happy to discuss any concerns or queries that you may have. You can contact us on +66(0)2-251-8666 or fill in your details in the form below and submit.
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text f_post_font_family=”file_2″ post_color=”#666666″ f_post_font_size=”24″]
[ninja_form id=2]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]
